Page 33 - NAMAH-Apr-2021
P. 33
Namah Multi-sensory approaches of music in the brain — I
motor preparation and movement sequences. external globus pallidus increases. This is
Along with various types of movements, why PD patients have tremors and difficulties
the putamen also affects many types of in performing voluntary movements and face
learning, including reinforcement learning a difficult time in motor planning.
and implicit learning. The auditory advantage
is almost eliminated if visual rhythms are Treatment plan
presented using continuous stimulation. Some
evidence suggests that the deaf possess some Parkinson’s disease is characterised by severe
advantage in tracking visual rhythms. The movement impairments that usually cause
strength of direct visual input to auditory- gait disorders which include small steps, lower
motor pathways is likely enhanced in deaf cadence, reduced gait speed and sometimes
individuals. Many studies have used EEG festination and freezing. The research studies
to assess neural entrainment to the beat. of Dr. M. Thaut described that rhythm and
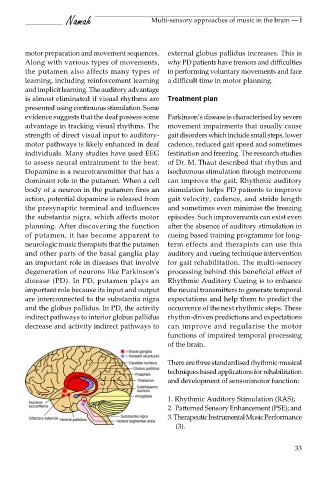
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that has a isochronous stimulation through metronome
dominant role in the putamen. When a cell can improve the gait. Rhythmic auditory
body of a neuron in the putamen fires an stimulation helps PD patients to improve
action, potential dopamine is released from gait velocity, cadence, and stride length
the presynaptic terminal and influences and sometimes even minimise the freezing
the substantia nigra, which affects motor episodes. Such improvements can exist even
planning. After discovering the function after the absence of auditory stimulation in
of putamen, it has become apparent to cueing based training programme for long-
neurologic music therapists that the putamen term effects and therapists can use this
and other parts of the basal ganglia play auditory and cueing technique intervention
an important role in diseases that involve for gait rehabilitation. The multi-sensory
degeneration of neurons like Parkinson’s processing behind this beneficial effect of
disease (PD). In PD, putamen plays an Rhythmic Auditory Cueing is to enhance
important role because its input and output the neural transmitters to generate temporal
are interconnected to the substantia nigra expectations and help them to predict the
and the globus pallidus. In PD, the activity occurrence of the next rhythmic steps. These
indirect pathways to interior globus pallidus rhythm-driven predictions and expectations
decrease and activity indirect pathways to can improve and regularise the motor
functions of impaired temporal processing
of the brain.
There are three standardised rhythmic-musical
techniques based applications for rehabilitation
and development of sensorimotor function:
1. Rhythmic Auditory Stimulation (RAS);
2. Patterned Sensory Enhancement (PSE); and
3. Therapeutic Instrumental Music Performance
(3).
33